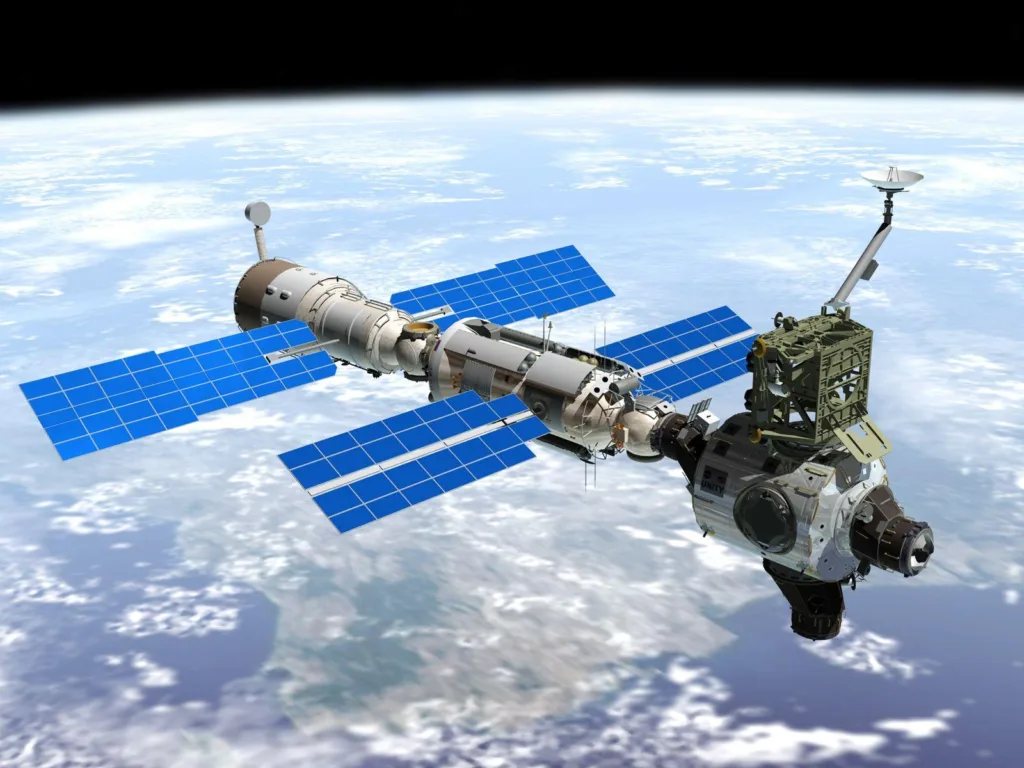
The vast expanse of the cosmos, once a realm reserved for exploration and scientific curiosity, is becoming an arena of strategic significance. The emergence of space-related technologies, ambitious projects, and geopolitical rivalries has given rise to discussions about the potential for space wars. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the evolving landscape of space warfare, the race for supremacy, and the transformative future projects that promise to shape humanity’s cosmic endeavours.
Read More
I. The Dynamics of Space Warfare
1. The Militarization of Space:
As nations become increasingly reliant on satellites for communication, navigation, and surveillance, the militarization of space has become a reality. Satellites are vulnerable targets, and nations are developing capabilities to protect their assets and, in some cases, to interfere with those of adversaries.
2. Anti-Satellite (ASAT) Weapons:
The development of anti-satellite weapons represents a significant aspect of space warfare. ASAT capabilities can disrupt communication networks, disable reconnaissance, and potentially escalate conflicts on Earth. The testing and deployment of such technologies raise concerns about the weaponization of space.
3. Space Cybersecurity:
The interconnectedness of space systems introduces a new frontier for cyber threats. Protecting space assets from cyber attacks is crucial, as a breach could compromise the functionality of satellites and disrupt essential services.
4. The Treaty Landscape:
International agreements, such as the Outer Space Treaty of 1967, aim to prevent the militarization of space. However, evolving technologies and geopolitical tensions have prompted discussions about the need for updated treaties that address contemporary challenges.
II. The Great Powers’ Space Ambitions:
1.United States
The United States, a pioneer in space exploration, has maintained a strategic advantage in space capabilities. Initiatives like the Space Force demonstrate a commitment to securing American interests in space and protecting critical assets.
2. China’s Rapid Advancements:
China has made significant strides in space exploration and technology. From lunar missions to the development of advanced satellites, China’s space programme is expanding rapidly. China’s space ambitions are closely tied to its geopolitical aspirations.
3. Russia’s Continued Influence:
Despite economic challenges, Russia remains a key player in space exploration. The country’s expertise in rocket technology and its commitment to space activities position it as an influential actor in the evolving space landscape.
4. Emerging Players and Collaborations:
Beyond the traditional space powers, emerging players like India, the European Union, and private space companies are contributing to the diversification of space activities. Collaborations between nations and private entities are shaping a more interconnected space ecosystem.
III. Future Projects Shaping Space Exploration:
1.Artemis Programme:
NASA’s Artemis programme aims to return humans to the Moon, including the first woman and the next man, by the mid-2020s. This lunar exploration initiative sets the stage for future crewed missions to Mars, marking a new era of deep space exploration.
2. Mars Colonisation:
Visionary projects envision the colonisation of Mars. Humanity’s ambition to become a multi-planetary species is signalled by SpaceX’s Starship, designed for interplanetary travel, and NASA’s plans for a sustained human presence on Mars.
3.Lunar Gateway and International Collaboration:
The Lunar Gateway, a planned space station orbiting the Moon, represents a collaborative effort involving NASA, international space agencies, and commercial partners. This project aims to facilitate lunar exploration and serve as a stepping stone for future deep space missions.
4.Space Tourism:
Commercial space tourism is on the horizon, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin pioneering efforts to make space travel accessible to civilians. As the industry develops, it could open new frontiers for exploration and economic opportunities.
IV. Environmental and Ethical Considerations
1. Space Debris Management:
The increasing number of satellites and space missions contributes to the growing issue of space debris. Sustainable practices and responsible space exploration become imperative to mitigate the environmental impact of human activities in orbit.
2. Ethical Use of Space Technologies:
The ethical considerations of space exploration extend to issues such as privacy, data security, and the responsible use of advanced technologies. Evolving space capabilities necessitate the establishment of ethical frameworks to guide the responsible conduct of space activities.
V. Space Diplomacy
1. Cooperation vs. Competition:
Cooperation and competition will shape the future of space exploration. While geopolitical rivalries persist, international collaboration in space endeavours holds the potential to foster diplomatic ties and shared benefits.
2. United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA):
UNOOSA plays a vital role in coordinating international efforts related to outer space. Strengthening diplomatic channels and promoting dialogue through platforms like the UN can contribute to the peaceful use of outer space.
VI. The Role of Private Entities
1. SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Beyond:
Private companies, led by SpaceX and Blue Origin, have disrupted the traditional space industry. Their innovations, reusable rocket technology, and ambitious projects are driving competition, reducing costs, and expanding access to space.
2. Commercial Space Stations:
As space tourism and commercial activities in orbit advance, the concept of commercial space stations is gaining traction. Private companies aim to establish platforms for research, manufacturing, and leisure in Earth’s orbit.
VII. The Ethos of Human Exploration
1. Beyond National Borders:
The ethos of human exploration transcends national borders. As humanity ventures into the cosmos, the principles of collaboration, environmental stewardship, and ethical conduct must guide our collective journey into space.
2.Inspiring Future Generations
The awe-inspiring nature of space exploration has the power to captivate imaginations and inspire future generations. Educational initiatives and outreach programmes can cultivate a passion for science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, ensuring a legacy of exploration.
VIII. Conclusion: Navigating the Cosmos with Purpose:
As space becomes a theatre for technological advancements, geopolitical manoeuvring, and visionary projects, humanity stands at the threshold of a new era in cosmic exploration. The balance between competition and collaboration, the ethical use of space technologies, and the pursuit of ambitious projects will shape the future of space exploration. As we navigate the cosmos with purpose, the lessons learned from our celestial endeavours will echo through generations, leaving an indelible mark on the human spirit’s quest for understanding and discovery.
Some general FAQs about Space
Potential space expeditions could land on the moon, visit other worlds, and create fuel and mining colonies, particularly in the asteroid belt. Robotic probes will carry out physical exploration outside the solar system for the foreseeable future.
It’s possible that humanity will be preparing to send unmanned interstellar spacecraft into neighbouring star systems by 2050. Propulsion technology developments, like fusion or antimatter propulsion systems, enable spacecraft to embark on extrasolar missions.
Ten times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope’s field of view is the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, scheduled for launch by NASA in October 2026. In order to investigate the south pole, China plans to launch Chang’e 7 into lunar exploration in late 2026.
The Big Crunch Theory is a symmetric theory of what will eventually happen to the cosmos. The Big Crunch Theory proposes that the universe’s average density will halt expansion and compress the cosmos, similar to how the Big Bang began as a cosmic expansion.
Not only is it tough to go to a new place, but moving entails starting over. Humans cannot breathe normally outside of Earth’s atmosphere, and they run the risk of dying from the sun’s intense heat. Essentially, the only thing that would save us would be to construct our own oxygenated and well-ventilated containment enclosures.
After 1014 (100 trillion) years, star formation will stop, leaving only degenerate stellar objects. If protons do not decay and the depletion of stellar-mass objects goes more slowly, this phase will continue.
Share this content: